Osteoporosis
-
 Nalamaree Team
Nalamaree Team
- 23 September 2025
Overview
Osteoporosis is a bone disease that weakens the bones, making them more likely to break. It is often called the "silent thief" because it can progress without any symptoms until a fracture occurs. Osteoporosis is a medical condition characterized by weakening of bones, making them fragile and more prone to fractures. Normally, bones are constantly being broken down and rebuilt in a process called remodeling. However, in osteoporosis, the rate of bone breakdown exceeds the rate of bone formation, leading to a decrease in bone density and strength.
Causes
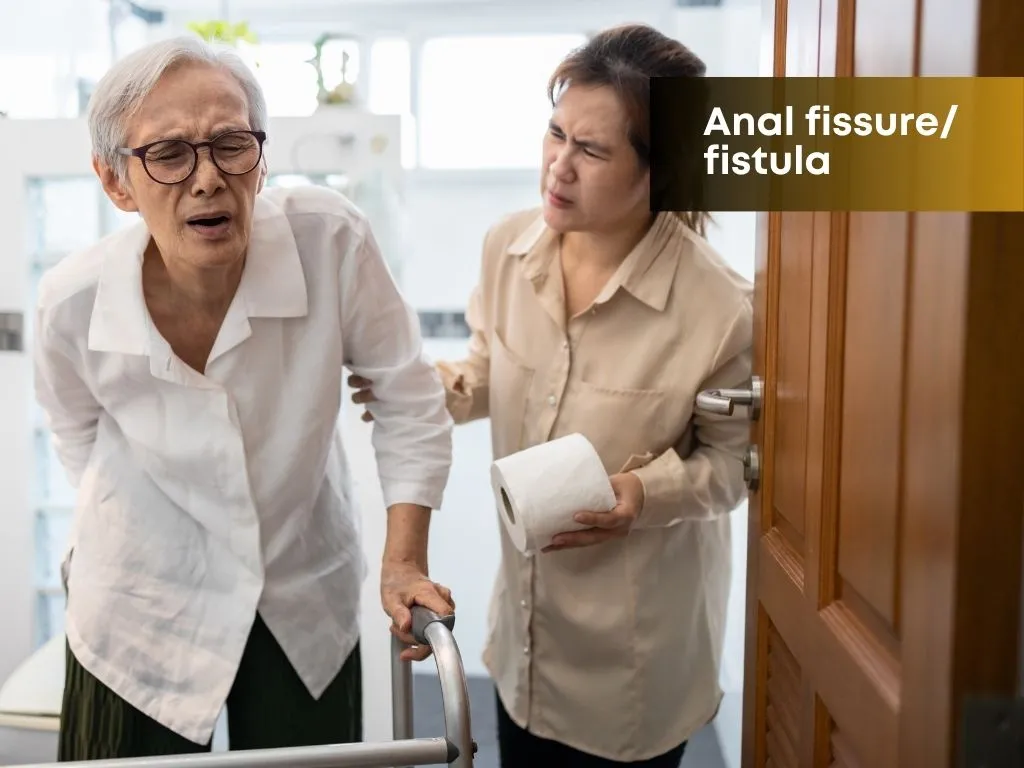
Osteoporosis often progresses without symptoms until a fracture occurs, typically in the hip, spine, or wrist. Fractures associated with osteoporosis can lead to significant pain, disability, and even mortality, particularly in older adults.
Symptoms
Osteoporosis often progresses without any symptoms until a bone fracture occurs. However, some individuals may experience signs and symptoms such as:
Treatment: Modern Medicine
Medications:
Treatment: Traditional Medicine
Caution



















.jpg.webp)
