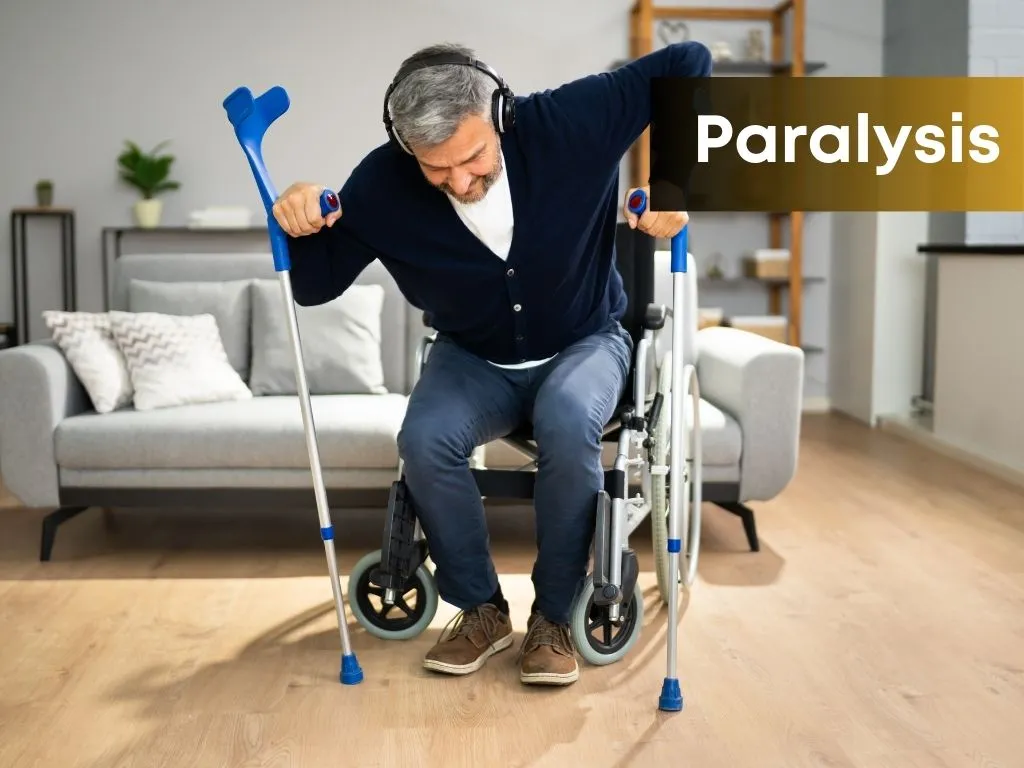
Overview
Paralysis is a loss of muscle function in part of your body. It can be temporary or permanent and can affect one or more muscles. Paralysis can result from damage to the nerves that control muscles, spinal cord injuries, stroke, or other conditions that disrupt the communication between the brain and muscles.
Causes
Spinal Cord InjuryStrokeTraumatic Brain Injury (TBI)Neurological DisordersInfections and DiseasesGenetic ConditionsAutoimmune DisordersTumors
Symptoms
Loss of Muscle ControlWeaknessLoss of SensationSpasticity or RigidityChanges in ReflexesDifficulty with CoordinationChanges in Bowel and Bladder FunctionDifficulty Breathing or Swallowing
Treatment: Modern Medicine
Medications: Depending on the specific condition causing paralysis, medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms, address underlying causes, or prevent complications. These medications may include:
Anti-inflammatory drugs.Pain relievers.Muscle relaxants.Blood thinners.Occupational TherapySpeech TherapyAssistive DevicesFunctional Electrical Stimulation (FES)Surgical InterventionsRegenerative Medicine
Treatment: Traditional Medicine
Nutritional SupplementsPsychological SupportMind-Body PracticesHerbal Remedies
Caution
Preventing Pressure SoresPreventing Muscle ContracturesPreventing Respiratory ComplicationsPreventing Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Prevention
Preventing Traumatic Injuries:
Wear seat belts while driving or riding in vehicles.Use appropriate safety gear, such as helmets.
Preventing Stroke:
Maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly.Manage medical conditions that increase stroke risk.Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Preventing Spinal Cord Injuries:
Practice safe driving habits, such as avoiding distractions, obeying traffic laws.Take precautions to prevent falls, particularly in older adults.Use proper lifting techniques to prevent back injuries.Wear appropriate protective gear when participating in high-risk activities.
Preventing Neurological Disorders:
Maintain overall health and well-being by following a healthy lifestyle.Manage medical conditions that can affect neurological health.Follow safety guidelines for recreational activities.
 Nalamaree Team
Nalamaree Team


















.jpg.webp)
